How the US Federal Reserve Affects Real Estate
A Guide for Investors and Homebuyers
The intricacies of financial institutions like the US Federal Reserve can seem detached from our day-to-day lives. However, the mechanisms and decisions of the Fed notably influence various sectors, with real estate being a significant one. For real estate investors, homebuyers, and financial analysts, understanding how the Federal Open Market Committee’s (FOMC) actions drive change in the property market is part of what you need to know to make informed decisions. In this article, we’ll decode the Federal Reserve’s role and domino effect on real estate.
The FOMC and Its Role in Economic Policy
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) is a branch of the Federal Reserve System responsible for overseeing the nation’s open market operations. This committee meets eight times a year to discuss and adjust monetary policies that affect the economy’s flow of money and credit.

The FOMC’s most watched activity is setting the federal funds rate. This is the interest rate at which depository institutions lend reserve balances to other institutions overnight.
The Reserve Requirement
For this to make sense, you should know a little bit about how commercial banking works.
Federal law requires all commercial banks to maintain an interest-bearing account with the Federal Reserve. The amount in this account is based on a percentage of the bank’s total deposits. It’s called the “reserve requirement.” The monies are intended to cover depositor withdrawals and other debt obligations.
If the account has more funds than the reserve requirement, that bank can lend its excess to another bank reporting a shortfall. The interest rate for this loan is the federal funds rate.
The Federal Funds Rate
While this sounds highly technical, it acts as a base interest rate influencing many other economic rates, including short-term loans on credit cards and consumer loans. It also impacts consumer and investor confidence in the stock market and can influence activity in the short-term.
The FOMC looks at the most recent unemployment, inflation, and economic growth data to set the rate. They then adjust the federal funds rate to meet their mandates: fostering maximum employment and price stability through controlling inflation.
Understanding Basis Points and Their Importance
A basis point is a unit of measurement used in finance to describe a percentage change in the value or rate of a financial instrument. One basis point equals 0.01% (1/100th of a percent) or 0.0001 in decimals. In the context of the Federal Reserve’s policies, basis points are used to express changes in interest rates.
When the FOMC adjusts interest rates, it is by a certain number of basis points. For instance, if the committee raises rates by 25 basis points, it means the rate has increased by 0.25%.
The 10-Year Treasury Yield: A Benchmark for Mortgages
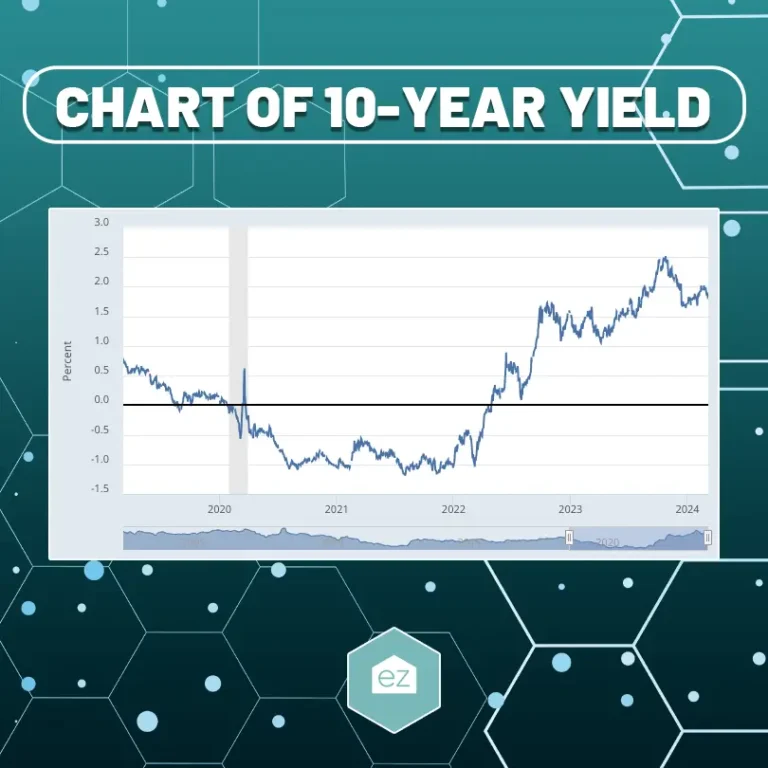
The 10-Year Treasury Yield is a crucial benchmark for interest rates in the United States. It represents the yield on the 10-year government bond issued by the US Treasury Department and is often used as a reference point for long-term mortgage rates.
The Federal Reserve’s actions can significantly impact the 10-Year Treasury Yield, causing it to rise or fall. For example, if the FOMC raises interest rates, investors may seek to sell off their low-yielding long-term bonds, causing the yield to increase. This increase can then lead to higher mortgage rates for homebuyers.
The 10-Year Treasury Yield is considered a benchmark that reflects long-term US interest rates. It is closely followed in real estate markets as a predictor of mortgage interest rate movements. When the 10-year Treasury Yield rises, it often leads to an increase in mortgage rates. Conversely, a dip in the Treasury Yield can lower borrowing costs for homebuyers and property investors.
The Trickle-Down Effect on Real Estate
Note that changing the Federal Funds Rate takes time to impact the 10-year Treasury Yield. While a change may affect the next day’s stock market, the Treasury Yield will feel impacts 4-8 weeks down the road and the mortgage rates after that.
Higher interest rates typically increase the cost of borrowing. For real estate investors and homebuyers, this translates to higher mortgage rates. This can dampen demand for property as the cost of financing goes up. Conversely, when the Federal Reserve cuts rates, we usually see an increase in real estate market activity due to the cheaper borrowing costs.
Consider what happened in the pandemic era. Near record-low borrowing costs encouraged home-buying as consumers rushed to take advantage of the rates. As the era ended and interest rates rose in response to inflation, mortgage applications and buying decreased considerably.
Another fallout of higher borrowing costs? It can impact property values. Buyers have less purchasing power when it becomes more expensive to carry a mortgage. A 1% rate difference on a 30-year fixed-rate $300,000 home loan amounts to about $200 monthly. Since this reduces what buyers can afford, it puts downward pressure on property prices. On the other hand, low interest rates tend to support property values, as borrowing is more affordable.
For real estate investors, the cost of capital is a critical component of any investment decision. Keeping an eye on the Federal Reserve’s interest rate policy helps investors anticipate changes in the leverage cost and manage risk.
Tracking the Treasury Yield
For those in the real estate business, keeping a pulse on the 10-Year Treasury Yield is essential. It gives clues about the future direction of mortgage rates. Savvy investors and buyers watch the yield curves and use these insights to predict the best timing for funding their real estate purchases.
It’s also worth noting that while the Fed’s influence is substantial, other economic factors also drive changes in real estate financing and property value. These include inflation, employment rates, and the economy’s overall health. Supply and demand is another contributing factor for local real estate markets.
Watching the Federal Reserve
Through adjusting the federal funds rate and its effects on the 10-Year Treasury Yield, the Fed indirectly guides the cost of mortgages and the affordability of investing in property. For players in the real estate market, monitoring the Fed’s policy decisions is not merely a practice—it’s an imperative part of staying ahead in an industry where the tide can shift with each FOMC announcement. See the FOMC meeting schedule to know when you can expect an update.
Start Your Home Search
Preston Guyton
Share this Post
Related Articles
Real Estate Information
The Role of a Buyer’s Agent in Real Estate Transactions
Real Estate Information
Who’s Buying What? Exploring Home Buyer Generational Trends
Real Estate Information
Your EZ Guide to Idaho Property Taxes
Real Estate Information





